
Heat strengthened glass (HSG) is a type of glass that has been subjected to a heat treatment process that increases its strength and durability. This process, typically performed by specialized heat treated glass suppliers, involves heating the glass to a high temperature and then rapidly cooling it. This causes the surface of the glass to be in compression, while the interior is in tension. This creates a stronger glass that is more resistant to breakage than annealed glass.
Heat strengthened glass is typically about twice as strong as annealed glass of the same thickness. It is also more resistant to thermal stress and impact. This makes it a good choice for applications where safety and durability are important, such as:
Doors and windows
Shower enclosures
Furniture
Appliances
Automotive glass
Due to its enhanced properties, heat strengthened glass is often used as a type of custom architectural glass in various construction and design projects.
Glass Thickness | 5mm - 6mm - 8mm - 10 mm - 12mm ; |
Glass Color | Clear, blue, bronze, green, gray, tinted reflective, ultra clear, online/offline lowe etc; |
Min size | 300x300mm; |
Max size | 3300x6000mm; |
Minimal radius | > 600mm; |
Shape in | Single curved, double curved, various curved; |
Extend processing | Acid, AR, AG coating, silk screen/digital printing, hole, notch etc; |
Curved glass refers to glass that has been shaped or bent into a curved or rounded form during the manufacturing process. This type of glass is used in various architectural and design applications to create aesthetically pleasing and innovative structures. Evergreen curved glass can be produced through different techniques, each offering unique advantages and characteristics.
1. Hot Bending: In hot bending, flat glass is heated to its softening point, and then it is shaped or bent into the desired curved form using a mold. This process requires precision control of temperature and timing to achieve the desired curvature. After shaping, the glass is gradually cooled to anneal and strengthen it.
2. Cold Bending: Cold bending involves curving the glass while it is in a cold state. This method is often used for simpler curves or gentle bends. Cold bending is less energy-intensive than hot bending, but it may have limitations in terms of the complexity of shapes that can be achieved.
3. Laminated Curved Glass: Laminated curved glass is created by bonding multiple layers of curved glass together with an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB). This not only enhances the strength of the glass but also provides additional safety benefits. In case of breakage, the interlayer holds the glass fragments together, reducing the risk of injury.
4. Double Curvature: Some curved glass applications require double curvature, where the glass is curved in two dimensions. This is often seen in complex, free-form designs such as the curved surfaces of modern architectural structures.
Evergreen architectural glass suppliers provide the following custom choices:
1. Size availability of custom bent glass for sale:
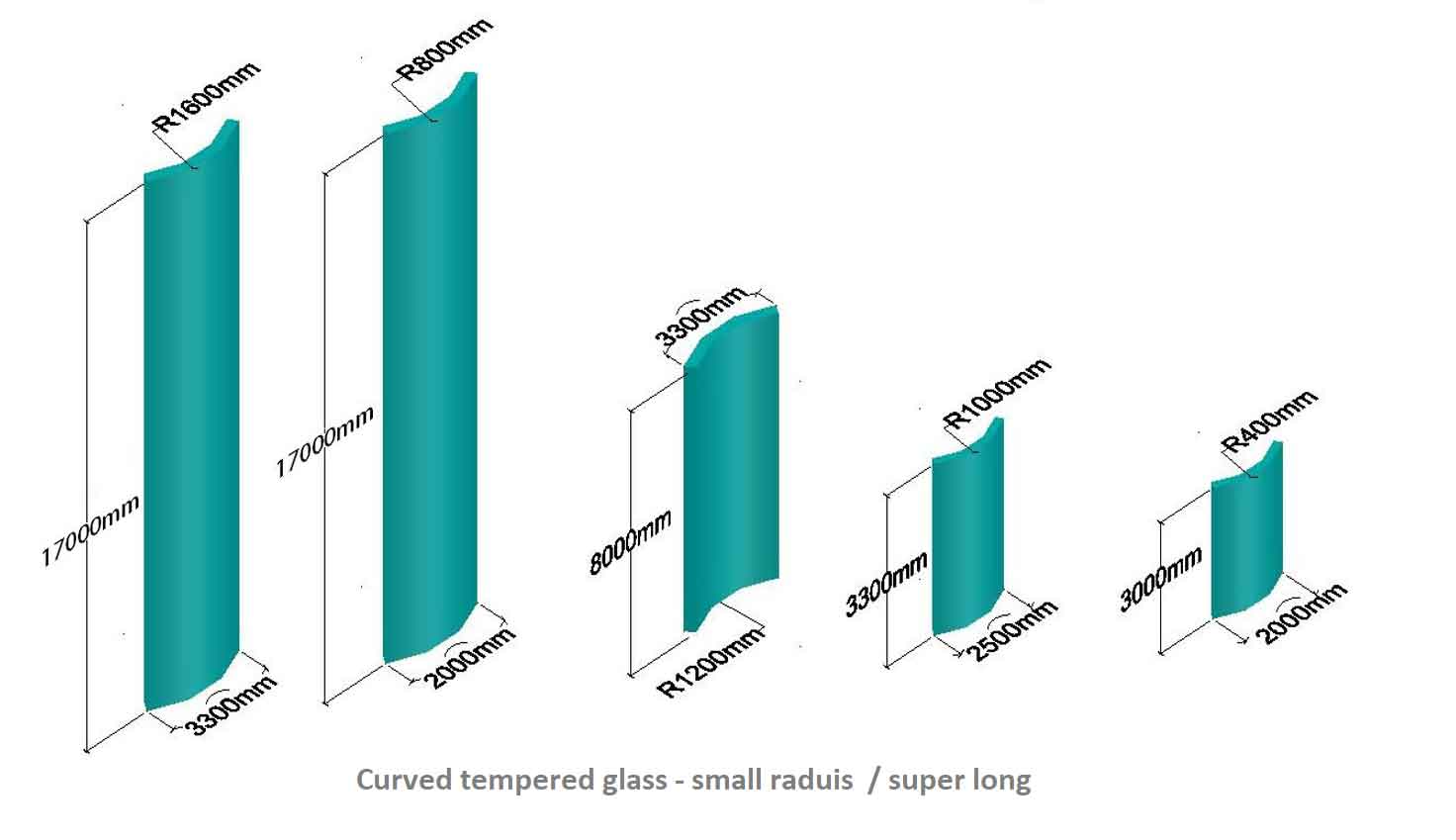
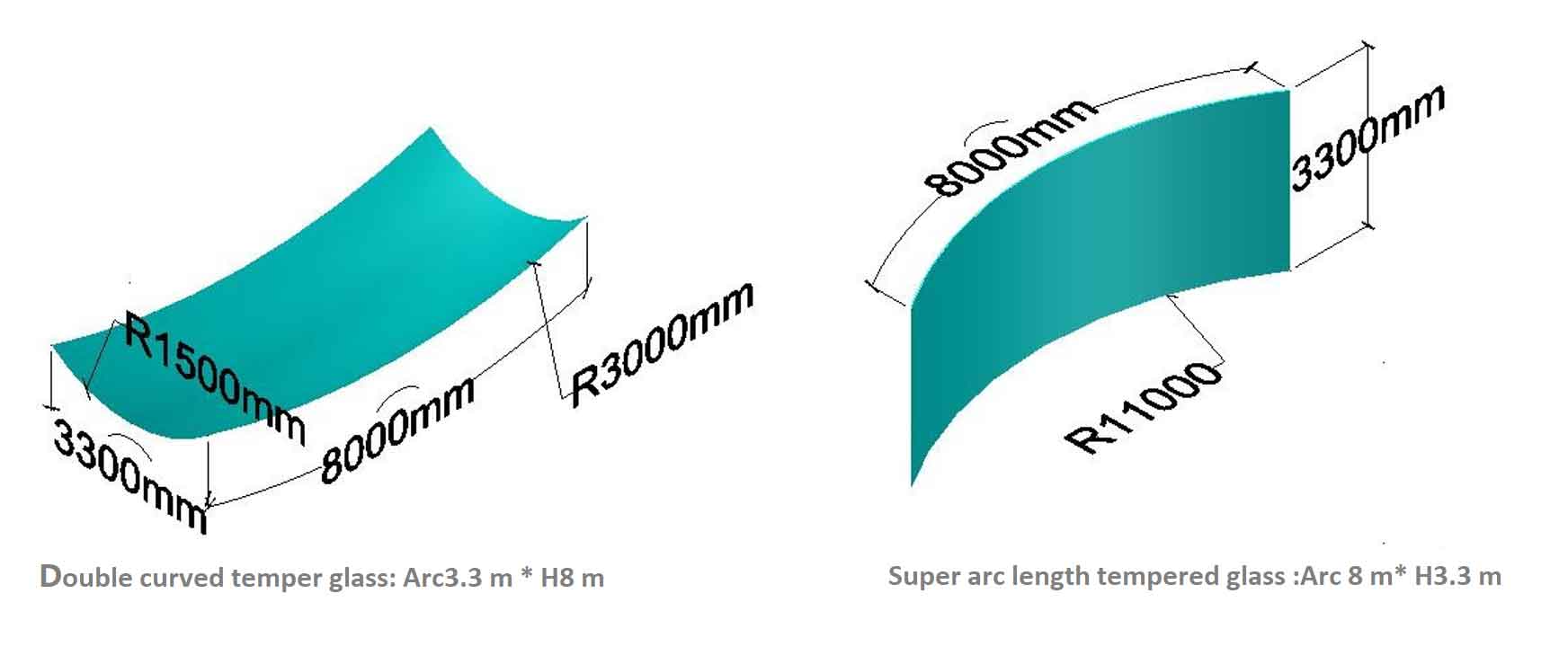

2. Shape availability of custom bent glass for sale:
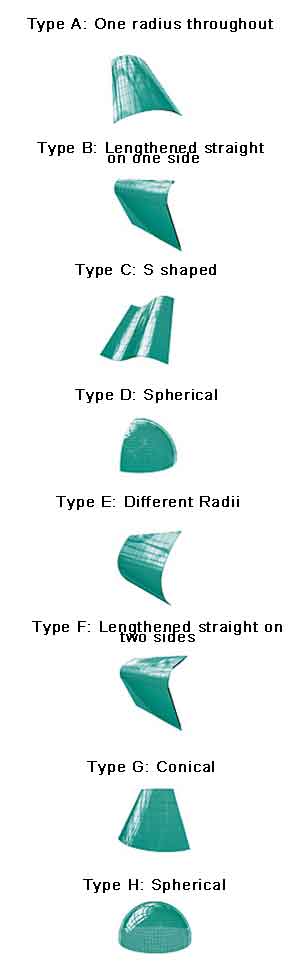
1. Architectural Glazing: Curved glass is used in the construction of modern buildings, providing unique and aesthetically pleasing facades, windows, and skylights.
2. Automotive: Curved glass is commonly used in automobile windshields and windows.
3. Furniture: It is employed in the design of curved glass tables, shelves, and other furniture pieces.
4. Displays: Curved glass is used in electronic devices like curved TVs and computer monitors.
5. Art and Design: Curved glass is often incorporated into artistic installations and sculptures.
The choice of the manufacturing method and the type of curved glass depends on the specific requirements of the project, including the desired curvature, safety considerations, and aesthetic preferences.
Curved glass can be used for windows, doors, curved glass curtain wall, and other architectural elements.
Curved glass can be used for tabletops, shelves, and other furniture elements.
Curved glass can be used for windshields, side windows, and rear windows.
Curved glass can also be used in a variety of other applications, such as aquariums, display cases, and lighting fixtures.
Pls contact us if you have any inquire or questions, thank you.
No.12111, JINGSHI ROAD, LIXIA DIST, JINAN CITY, SHANDONG PROVINCE, CHINA